
OSPF Explained Step By Step With Practicals From CCNA To CCIE Level
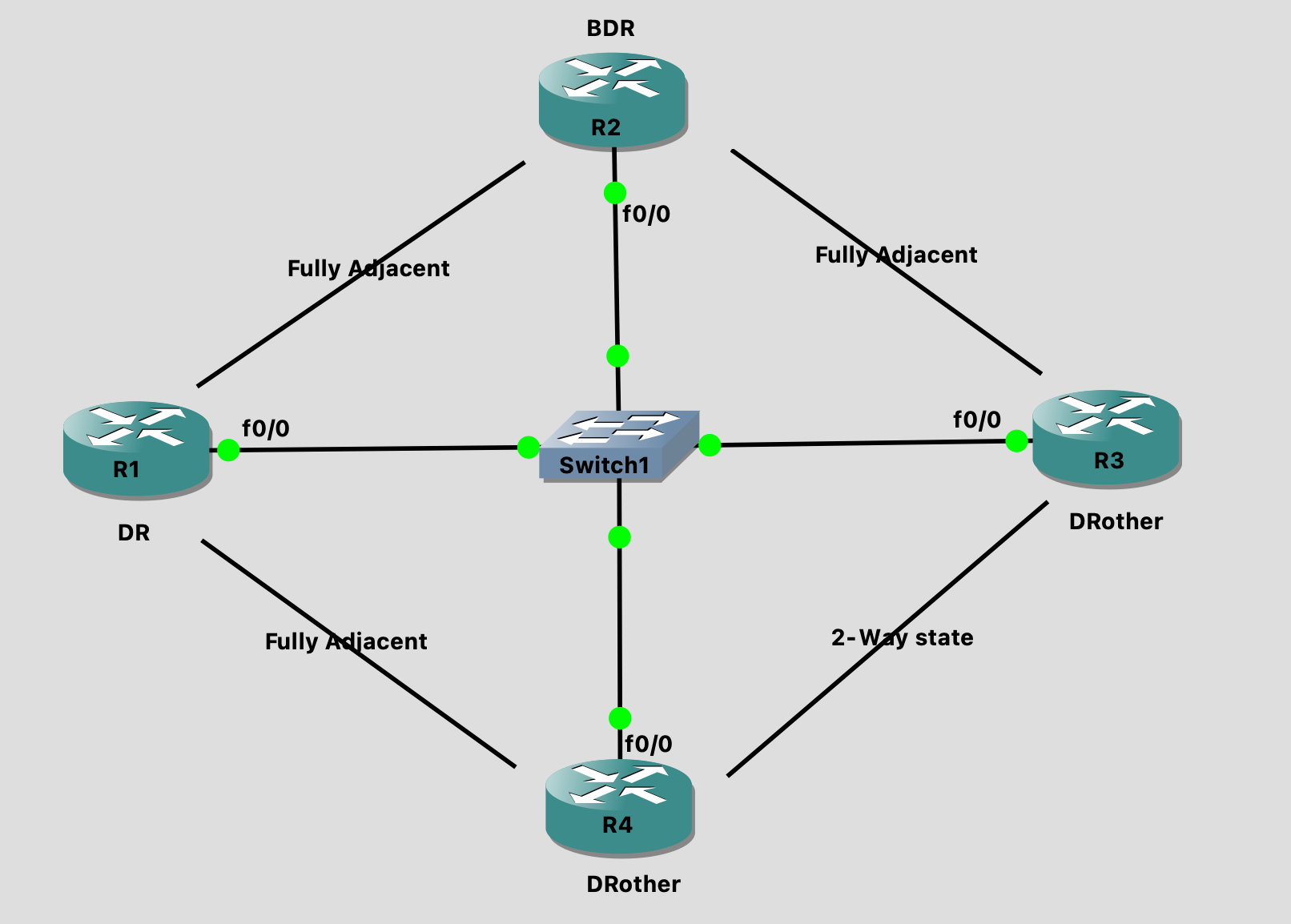
* Neighborship:
the routers who stuck in 2-way state
They do not have power to share updates to each other
DRother routers are considered in Neighborship state
DRother to DRother
Whenever any DRother gets a update they send the update to DR on multicast address 224.0.0.6
* Fully adjacent:
The routers who pass all the states and goes in Full state
Fully adjacent routers can share updates to each other
DR to BDR
DR to DRother
BDR to DRother
can be any IP (existing or non existing)
1-manually defined //router-id 1.1.1.1
2-highest loopback
To present itself in an area and to tell the identity of the database, the router-id is forwarded in the hello packet and should be unique because two routers cannot have the same identity.
Whenever we enable OSPF on a router, first task is always to select a router ID, if router do not find any active ipv4 address in global routing table it throw a error not to start OSPF process
| Router ID election process |
|---|
| R1(config)#router ospf 1 %OSPF-4-NORTRID: OSPF process 1 failed to allocate unique router-id and cannot start |
We can manipulate the router-id by using a command in router configuration mode, if the router is having pre-existing neighbor then u have to clear OSPF process first, then the new router-d will will be in effect.



