
Master EIGRP for a successful Cisco certification journey
Now let’s discuss more details on metric and other ingredients used in metric
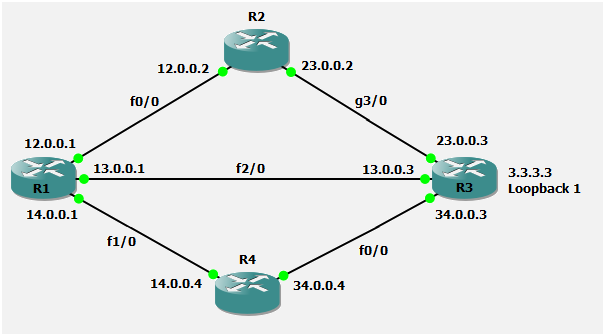
To reach Router R3 loopback address from R1 we have 3 paths available, on is direct to R3, other is via R2 and last one is via R4
First of all router calculate metric of all available path and that is called as CD (Computed distance)
*R1 to R3 is 156160
*R1 to R3 via R2 is 156416
*R1 to R3 via R4 is 158720

Now the EIGRP router checks lowest CD and lowest CD will mark as FD (feasible distance)
FD is also referred as successor or we call it best path metric, so now we have best path metric via R3 is 156160.
In output we can see one more metric value after CD, that is advertised by neighbor router and that is considered as AD(Advertised distance) or RD(Reported Distance), for neighbor that is FD to reach that destination.

So till now we have discussed few new information:
CD: Computed distance
FD: Feasible distance
AD: Advertised distance
RD: Reported distance
Successor: best path metric
After this calculation router try to find the backup path with feasibility condition, and for that we have a condition: Router FD should be greater than other path RD value FD > RD
So in our Lab FD is 156160 & RD via R2 is 130816, via R4 is 156160
So if we check condition via R2: FD > RD
156160 > 130816
Condition is true and router will use this path as a backup path
If we check condition via R4: FD > RD
156160 > 156160
Condition is false here and cannot be considered as backup path on this router.
And the same feasibility condition (Loop free backup path condition) works to prevent loop in EIGRP topology.
When we use EIGRP so total we use 4 tables:
Neighbor table
Routing Table
Topology table
Topology all link table
We have done about Neighbor table so now we will do more focus on Routing table, Topology table & Topology all link table
As we know initially EIGRP router does a calculation of CD (Computed distance) & gets RD (Reported distance) from Neighbor.
After these calculations Device put all the information of CD and RD in Topology all link table.
Command: Sh ip eigrp topology all-links (output is altered for network 3.0.0.0)
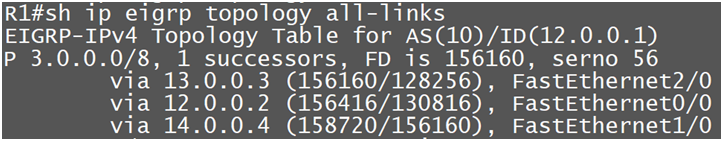
Topology all-links table maintain all the best router, backup router and the routes who did not pass feasibility condition
After this step EIGRP router pick Best and Backup router from topology all-link table and put in EIGRP topology table
So the topology table just maintains Best and Backup path for a route.
Command: Sh ip eigrp topology (output is altered for network 3.0.0.0)
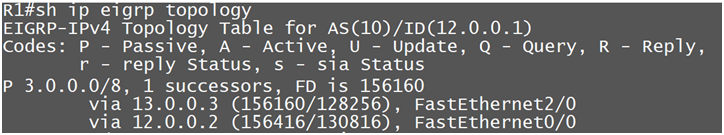
And here we can see only best and backup path Finally Router pick only best path and maintain in Routing table
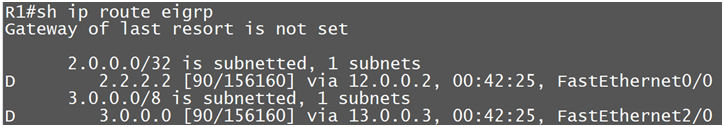

Now we will discuss how the EIGRP routers install routes in Topology table after getting updates and how they decide which route needs to be uninstalled.
Whenever a router gets a update from a neighbor, first router match the hop count received in EIGRP update packet with its own configured values
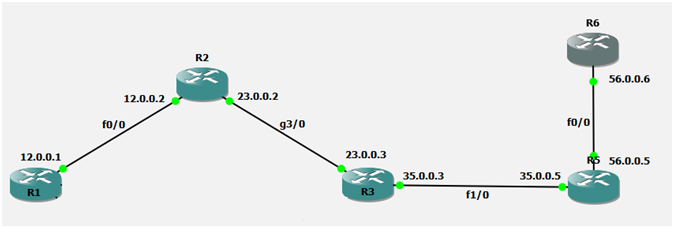
*Here R1 will get update from R5 and R6
*R5 will send a packet with hop count 0, R3 will receive it and will add 1, then it will send the same info to R2 with hop count 1 and R2 will add 1 more hop count then again it will send the update to R1 with hop count 2 and when R1 will receive It with add 1 more so at last it will be 3
*So whenever R1 will get update from R5 hop count should be configured 3 on R1
*And while getting update from R6 so hop count should be configured 4 on R1
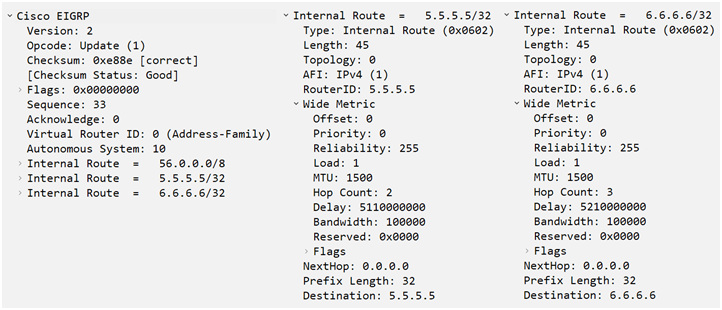
*So getting both routes in Routing Table of R1
*Now we will configure Hop count 3 and will see the output
router eigrp 10
metric maximum-hops 3
exit
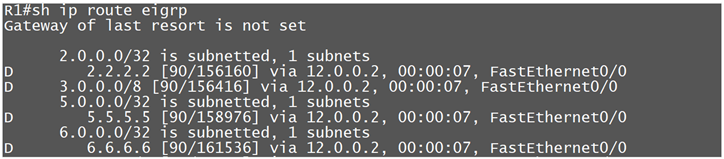
*Now R1 should get Routes only from R5 not from R6
Now after checking Hop-Count router checks Metric values to install the routes, as we have already discussed router check metric components to do metric calculation
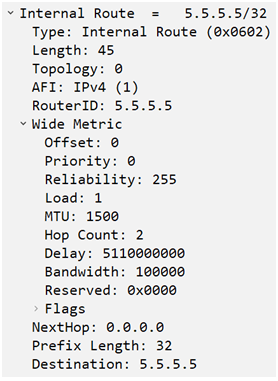
Once R1 will get check wide metric component and will add Delay and will compare Bandwidth and will use least bandwidth to do final metric calculation.
Whenever a router wants other routers to uninstall a route so it send the same update packet with modified details, whenever a router removes a route from EIGRP it sends a Query Packet with infinity delay, higher bandwidth and Hop-count 0 for the same prefix, and the same packets EIGRP router use to uninstall the prefix.
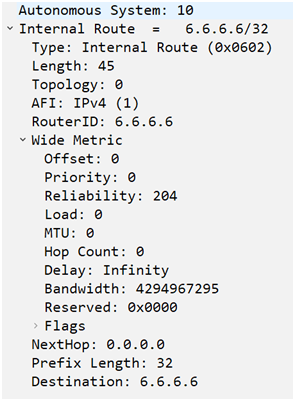
And other routers send same query packet to other routers to get positive or negative reply, that might get a new path for the prefix.







