
Master EIGRP for a successful Cisco certification journey
*Equal cost load balancing
*Unequal cost load balancing
Before starting Load-balancing concept you should know about EIGRP Topology and EIGRP Topology all link table, because these Two load balancing Mechanism will be using these two tables to work.
As we know EIGRP uses Topology All-Link table to store all the available Path for Prefixes, so we will perform Equal Cost Loadbalancing on Topology All-Link Table as it has all available path.
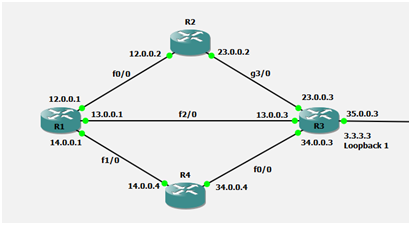
So here Router R3 Loopback will be used to perform Equal Cost Load-balancing on Router R1
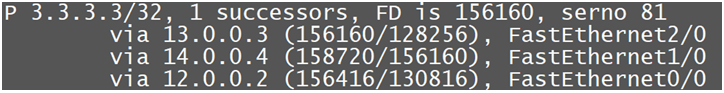
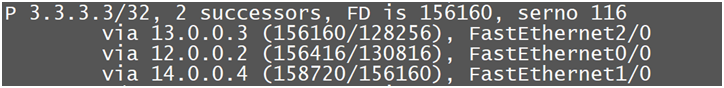
This output is of EIGRP Topology All-Link table for Prefix-3.3.3.3/32
As we can see we have 1 best path that has metric value 156160 and remaining 2 path has higher values and because of that 1st route is best
In Equal cost Load-Balancing we check the path that has very high metric value, so in our case the path via 14.0.0.4 has very highest metric value 158720
So now we need to make other 2 path metric equal to 158720 to perform Equal Cost Load-Balancing.
*After adding 2560 metric in best path that is via 13.0.0.03 it will be equal to 158720
*After adding 2304 metric in last path that is via 12.0.02 it will be equal to 158720
So now to perform Equal Cost Load Balancing we use offset list to add extra metric to the current one.
We use ACL to match the prefix and then apply with Offset list.
We have to be very careful while using offset list, we need to specify the interface along Offset list command otherwise it will be applicable for all the path and the metric will be added to all the path available.
Let’s add some metric using Offset list feature including Interface on which we want to add
1. Create ACL to match the Prefix
2. Go to EIGRP process
3. Run offset list command use ACL and add the extra metric in incoming Direction
4. With offset list command we will add interface on which we want to add extra metric
*R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
*R1(config-router)#router eigrp 10
*R1(config-router)#offset-list 10 in 2560 f2/0
*R1(config-router)#offset-list 10 in 2304 f0/0
*R1(config-router)#exit

Now in topology All-Link table we can see all 3 path has same metric value and all 3 path are the best path as we see 3 successors.
Lets check the same in Routing Table, Routing table should install all these three path as best path.

This is how we can achieve Equal Cost Load Balancing.
In Equal Cost Load Balancing we can use all available paths in Topology All Link table, but when we work with Unequal Cost Load Balancing we cannot use Topology All Link table, Unequal Cost Load balancing works on only Topology Table
Unequal Cost Load Balancing we can just achieve only on Best path and Backup path that’s why we only use Topology Table.
We use Variance Command to achieve Unequal Cost Load Balancing, in this calculation we try to increase the metric value more than backup path but this calculation happens in background only, we just see the output / best path in Routing Table with unequal metric.

This is the output of Topology all link
As we can see in this output we have best path and backup path, so now we will use variance command and will see how variance works
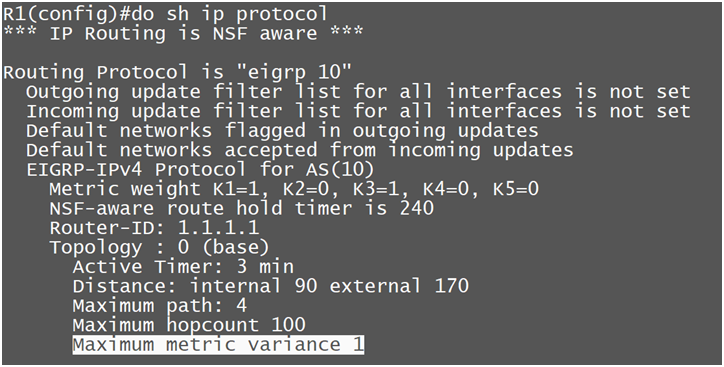
Variance has a Calculation method: by default Variance is set to 1 and we can change it from 1 to 128 also.
Unequal Cost Load Balancing Calculation: Best path metric * Variance >= Backup path metric So whenever we use Variance value, the router Multiply the Variance value with Best path metric and if the answer is equal or greater than the Backup path metric so it consider that path as best path and put that route also in routing table

So in our case if we change the Variance value to 2 it will be greater than the backup path metric (156416) and will be the best path then
So Let’s change the Metric Value.
*R1(config)#router eigrp 10
*R1(config-router)#variance 2
*R1(config-router)#exit
After running these commands here is the output

This is the output of Topology Table & we can see now both path are the best path as we can see 2 Successors

In Routing table also we can see 2 path as best path.
If We see the Topology All Link table so we find the calculation of using Variance 2 can be higher than the third available path, but Variance does not work on Topology All Link table/Non backup path.
Output of Topology All Link table and we see only 2 Path as best path because Variance does not work on non backup path.







